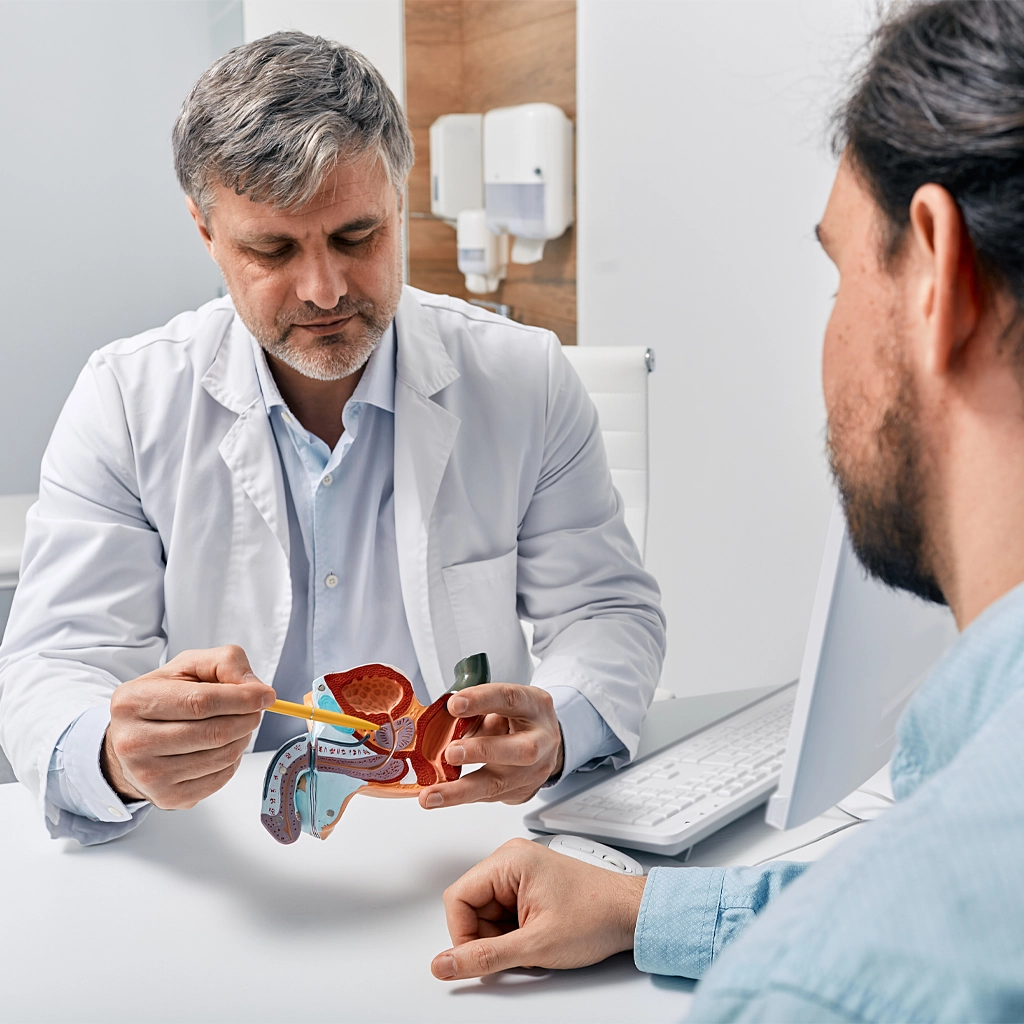
What are my treatment options?
Men with mild BPH symptoms can be treated with lifestyle changes, medication or supplements. Your doctor may also ask you to avoid taking certain medications like decongestants or certain antihistamines that can affect your prostate.
Those with more severe symptoms have many treatment options, including surgery. The most common surgery for an enlarged prostate is called transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), in which a surgeon cuts away a portion of the prostate to make it smaller. However, this surgery has potential side effects that include infection, urinary issues, sexual dysfunction and retrograde ejaculation.
Some urologists now offer a less invasive procedure called UroLift®. This involves implanting metal clips that physically lift the urethra away from the prostate. While it can alleviate urinary symptoms, it does not address the root cause of the problem—the enlarged prostate. As a result, it has not been shown to improve sexual function in men who have the procedure.
A minimally invasive, outpatient procedure called prostate artery embolization (PAE) was approved by the FDA in 2018 and has become an excellent option for most men with BPH. It effectively shrinks the prostate, reducing or eliminating urinary symptoms. It is also shown to improve sexual performance. Click here if you’d like to take our quiz to see if you qualify for PAE.
You can learn more about PAE by clicking here »